82 Graph an absolute value function
The most significant feature of the absolute value graph is the corner point at which the graph changes direction. This point is shown at the origin.
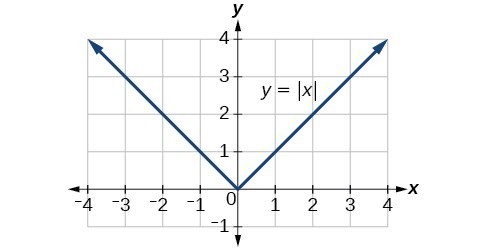
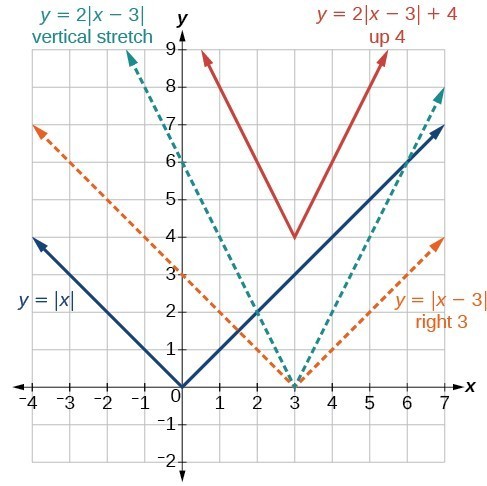
Figure 4 is the graph of [latex]y=2\left|x - 3\right|+4\\[/latex]. The graph of [latex]y=|x|\\[/latex] has been shifted right 3 units, vertically stretched by a factor of 2, and shifted up 4 units. This means that the corner point is located at [latex]\left(3,4\right)\\[/latex] for this transformed function.
Example 3: Writing an Equation for an Absolute Value Function
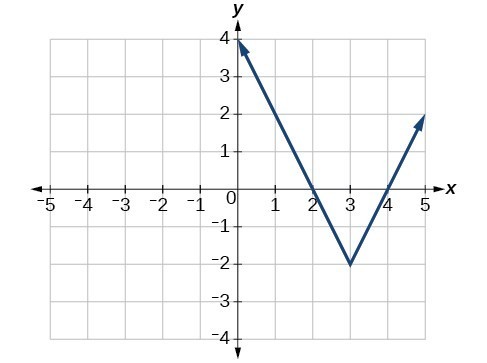
Write an equation for the function graphed in Figure 5.
Solution
The basic absolute value function changes direction at the origin, so this graph has been shifted to the right 3 units and down 2 units from the basic toolkit function.
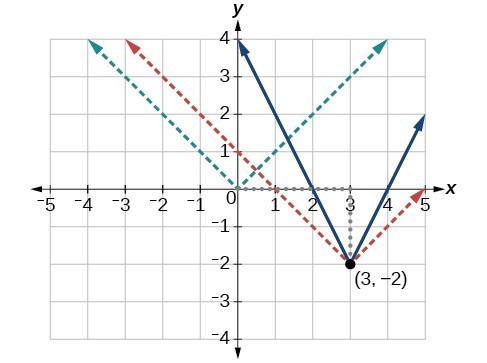
We also notice that the graph appears vertically stretched, because the width of the final graph on a horizontal line is not equal to 2 times the vertical distance from the corner to this line, as it would be for an unstretched absolute value function. Instead, the width is equal to 1 times the vertical distance.
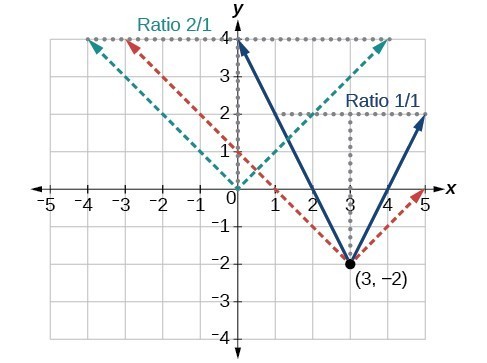
From this information we can write the equation
Q & A
If we couldn’t observe the stretch of the function from the graphs, could we algebraically determine it?
Yes. If we are unable to determine the stretch based on the width of the graph, we can solve for the stretch factor by putting in a known pair of values for [latex]x\\[/latex] and [latex]f\left(x\right)\\[/latex].
Now substituting in the point (1, 2)
Try It 3
Write the equation for the absolute value function that is horizontally shifted left 2 units, is vertically flipped, and vertically shifted up 3 units.
Q & A
Do the graphs of absolute value functions always intersect the vertical axis? The horizontal axis?
Yes, they always intersect the vertical axis. The graph of an absolute value function will intersect the vertical axis when the input is zero.
No, they do not always intersect the horizontal axis. The graph may or may not intersect the horizontal axis, depending on how the graph has been shifted and reflected. It is possible for the absolute value function to intersect the horizontal axis at zero, one, or two points.


Analysis of the Solution
Note that these equations are algebraically equivalent—the stretch for an absolute value function can be written interchangeably as a vertical or horizontal stretch or compression.